Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery maps the surface microwave radar reflectivity at resolutions from a sub-meter to 100 m depending on the particular SAR satellite and mode. Since a radar provides its own illumination, imagery is independent of the time of day. At typical radar frequencies, SARs can image through clouds, so SARs are considered "all-weather" instruments. Several geophysical parameters can be derived from SAR including sea surface wind speed.
Data Access
Product Overview
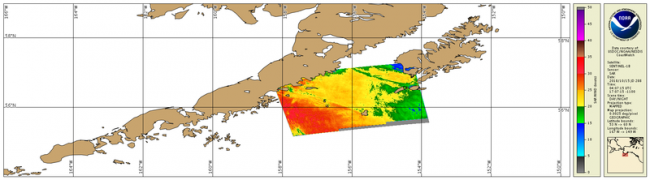
Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery maps the surface microwave radar reflectivity at resolutions from a sub-meter to 100 m depending on the particular SAR satellite and mode. Since a radar provides its own illumination, imagery is independent of the time of day. At typical radar frequencies, SARs can image through clouds, so SARs are considered "all-weather" instruments. Several gephysical parameters can be derived from SAR including sea surface wind speed.
For side-scanning SARs, the normalized radar cross section (NRCS) of the surface is proportional to the surface roughness on the scale of the radar wave length (from 3 to 30 cm). Ocean surface roughness on this scale is dependent on the local wind speed and direction. The higher the wind speed the larger the NRCS of the surface. The highest NRCS occurs when the radar look direction and wind direction are aligned and smallest when the radar looks cross wind.
The relationship between wind speed and direction and radar cross section is called the "geophysical model function." These functions are generally empirically determined.
Although we can predict an expected NRCS value for a given wind speed and direction, the reverse is not true. A specific NRCS value can be associated with many pairs of wind speed and direction. If we know the wind direction a priori, we can infer the wind speed.
For the operational SAR-derived wind speed products, we use the model directions from NOAA’s Global Forecast System (GFS) model on a 0.5 degree, latitude-longitude grid to initiate the retrievals. The wind speed retrievals are provided at 500 m resolution. These retrievals agree with independent wind speed estimates to better than 2 m/s.
Current users of these data are the US National Ice Center, the Alaska Weather Service, and the Naval Oceanographic Office.
A good review of SAR operational wind speed retrieval can be found at: http://tos.org/oceanography/assets/docs/26-2_monaldo.pdf
Product Details
| Product Families |
Sea Surface Roughness
Sea Surface Winds
|
|---|---|
| Measurements |
Normalized Radar Cross-Section
Sea Surface Wind Speed
|
| Processing Levels |
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
|
| Latency Groups |
0 Hours <= 24 Hours (NRT)
|
| Latency Details |
Less than 24 hours |
| Spatial Resolution Groups |
0 m <= 100 m
100m < 2km
|
| Spatial Resolution Details |
NRCS: Variable, 0-10 m |
| Data Providers |
NOAA
NESDIS
OSPO
|
Spatial Coverage
Selective Acquisitions
| Description |
Variable coverage. Observations taken as requested over targets of interest. |
|---|
Platforms
RadarSat-2
| Description |
RadarSat-2 |
|---|---|
| Platform Type |
Low Earth Orbit Satellite (LEO)
|
| Instruments | |
| Organizations |
CSA
|
| Orbital Altitude |
798 km
|
| Orbital Period |
100.7 minutes
|
| Orbital Inclination |
98.6°
|
| Equatorial Crossing Times |
06:00 desc
|
Sentinel-1
| Description |
Sentinel - 1A / 1B |
|---|---|
| Platform Type |
Low Earth Orbit Satellite (LEO)
|
| Instruments | |
| Organizations |
ESA
Copernicus
|
| Orbital Altitude |
693 km
|
| Orbital Period |
98.6 minutes
|
| Orbital Inclination |
98.18°
|
| Equatorial Crossing Times |
06:00 desc
|
Documentation
- Monaldo, F.M., C.R. Jackson, and W.G. Pichel. 2013. Seasat to RADARSAT-2: Research to operations. Oceanography 26(2):34–45, http://dx.doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2013.29
- SAR Marine User Manual (2004) Christopher Jackson and John Apel, Editors
