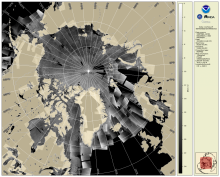
SAR Composite Arctic Imagery (normalized radar cross section)
The daily composite of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Normalized Radar Cross Section (NRCS) imagery covering the Arctic and sub-Arctic maritime regions over a period of one day are available at 1-km resolution. These high-resolution, weather- and time-agnostic measurements of surface backscatter contain detailed information tailored for sea ice classification purposes.